Hot Dip Galvanizing
Galvanizing is one of the most frequent methods of protecting steel from rusting. It involves a set of actions aiming at covering steel elements with a thin layer of zinc in order to protect them from corrosion resulting from atmospheric conditions. The electrochemical mechanism is used in this process. Zinc has a lower corrosive potential than steel and so it forms an anodic layer on the surface. The metalic layer protects steel by isolating it from the envioronment but it also oxidizes first and therefore protects the metal elements.
There are several methods of galvanizing steel constructions, among others thermal diffusion or hot-dip galvanizing. However, hot-dip galvanizing is the most widespread and known globally and in Poland. Zinc coating has better protective features of iron and steel especially in terms of its thickness.
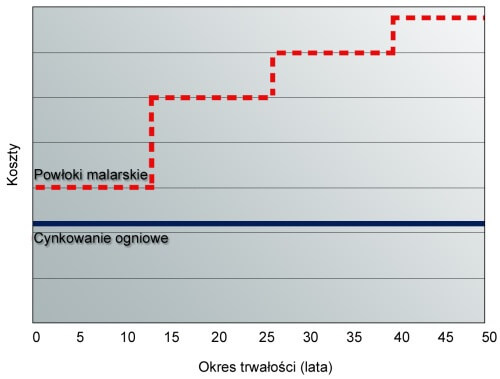
Hot-dip galvanizing is economical
Hot-dip galvanizing is the most economical method since galvanizing costs are covered only once. Zinc coating quarantees steel protection from rusting for many years without the need of renovation. However, the cost of only paint protection increases over time due to repairs every several years. Paint coating ages relatively fast and requires maintenance every 6 or 7 years on average.
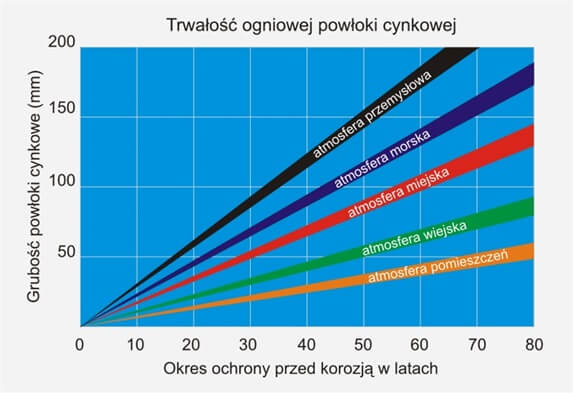
Hot-dip galvanizing is durable
The average durability of zinc coating is from 30 to 50 years. This period depends on the corrosive environment in which the construction is placed and on the thickness of zinc coating. It worth remembering that the thicker the coating is, the more protective it is. Worse protective features can be observed in very humid or saline environment.